Balancing Immunity with a Dietary Supplement Derived from Five Edible Plants for Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Author'(s): Sirithip Wiriyachitra, Pichaet Wiriyachitra* and Ampai Panthong
Asian Phytoceuticals Public Company Limited, Bangkok, Thailand.
*Correspondence:
Wiriyachitra P, Asian Phytoceuticals Public Company Limited, Thailand, Tel: +662 646 4882.
Received: 08 Jun 2024; Accepted: 13 Jul 2024; Published: 20 Jul 2024
Citation: Sirithip Wiriyachitra, Pichaet Wiriyachitra, Ampai Panthong. Balancing Immunity with a Dietary Supplement Derived from Five Edible Plants for Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin Immunol Res. 2024; 8(1): 1-3.
Abstract
The development of specific agents affecting T helper cell subpopulations has gained considerable attention in recent years, with natural products emerging as potential immune modulators for various diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study investigates the immunomodulatory effects of Arthrinox/BIM-A, a dietary supplement derived from five edible plants, namely black sesame, guava fruit, mangosteen aril, pennywort leaves, and soy protein, on the regulation of T helper cell subpopulations. Twelve healthy volunteers were divided into two groups, one receiving a placebo and the other taking Arthrinox/BIM-A capsules for 15 days. Blood samples were collected before and after the supplementation period, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated and stimulated to assess cytokine production. In the present study, we demonstrated that Arthrinox/BIM-A can modulate the immune cell functions by reducing the production of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-2, IL-17 and TNF-α. Arthrinox/BIM-A is therefore suggested as the food supplement for balancing immunity in the management of RA patients.
Keywords
Introduction
During the last decades, the development of specific agents affecting T helper cell subpopulations, i.e., Th1, Th3 and Th17 differentiation, has drawn special attention. Many natural products have been reported as effective agents for balancing the immune response by regulating the differentiation of T helper cell subpopulations. These products have the potential to be immune modulators for the treatment of various diseases, including infectious diseases, cancers, autoimmune diseases and arthritis.
In this study, we aim to study the immunomodulatory effects of Arthrinox/BIM-A, a dietary supplement consisting of five edible plants, namely black sesame, guava fruit, mangosteen aril, pennywort leaves and soy protein. We investigate the possible effect of Arthrinox/BIM-A on the control of T helper cell subpopulation differentiation.
Objective
The objective of this study is to investigate the possible effects of Arthrinox/BIM-A on the regulation of T helper cell subpopulations. The levels of various cytokines in blood collected from healthy donors before and after taking Arthrinox/BIM-A capsules for 15 days were compared.
Study Approaches
Study Subjects
- 12 healthy volunteers: 6 males and 6 females
- Age range: 20-55 years old
- The recruited volunteers were divided into 2 groups:
- Group 1: taking placebo; 6 subjects
- Group 2: taking Arthrinox capsule; 6 subjects
Blood Collection
Blood samples (5 ml, using heparin as an anticoagulant) were collected from each subject on day 0. According to their groups, subjects took either Arthrinox/BIM-A capsules or placebo (4 capsules/day) every day for 15 days. Afterwards, blood samples (5 ml, using heparin as an anticoagulant) were collected for the second time on day 16.
Study of the Effect of the Arthrinox/BIM-A Capsule on the Regulation of T Helper Cell Subpopulations
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from the collected blood using Ficoll-Hypaque gradient centrifugation. The PBMCs were then stimulated in vitro with or without anti- CD3 monoclonal antibodies (clones OKT3) and cultured for 24 hours at 37oC in a CO2 incubator. The cell culture supernatants were collected and centrifuged at 20,000 rpm for 2 minutes. The cell-free supernatants were separated and stored at -70°C for determination of cytokines.
Results
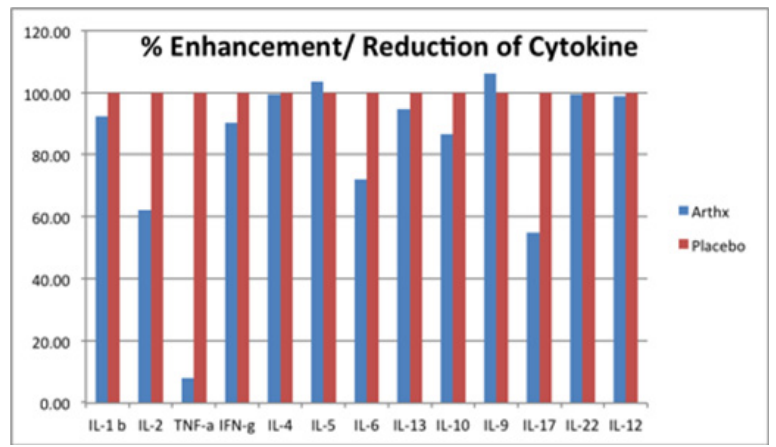
The stimulation indexes of various cytokines in subjects taking the Arthrinox/BIM-A capsules and placebo were calculated and compared. Normalization was performed using subjects taking the placebo. The percentage enhancement and reduction in subjects taking the Arthrinox/BIM-A capsules are shown in the figure below. The results indicate that Arthrinox/BIM-A capsules reduced the production of IL-2 and IL-17 and significantly reduced the production of TNF-α.
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is present at biologically significant levels in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial tissue and fluid, and seems to parallel the extent of both inflammation and bone erosion. TNF triggers several of the most central and critical events in acute and chronic synovial inflammation, ultimately leading to the tissue destruction characteristic of RA, including the induction of multiple additional cytokines and chemokines, the expression of adhesion molecules and increased levels of class I MHC determinants and the synthesis and release of proteases and prostaglandin E2 by synovial fibroblasts (which is important in the erosion of cartilage and bone) and synovial neoangiogenesis. Some data suggest that monocytes from patients with early RA hyperproduce TNF when activated. Taking all the data into consideration, one can reasonably conclude that TNF is one of the most important cytokines in the pathogenesis of RA [1].
RA is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by hyperplasia of the synovium and an excess of inflammatory cells, leading to progressive destruction of the joints. In RA, several cytokines, e.g., interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-17, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and granulocyte- macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), are involved in almost all aspects of articular inflammation and destruction. TNF-α has been considered a pivotal cytokine in the pathogenesis of RA, as significant clinical and laboratory evidence has been obtained by TNF-α blockade [2]. It has been reported that treatment of RA patients with infliximab (Remicade), a chimeric antibody specific for human TNF-α, substantially reduced the signs and symptoms of the disease, levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) in the serum, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) [3]. This result was confirmed in other multicenter placebo-controlled trials, together with the observation that therapeutic efficacy was enhanced when infliximab was coadministered with methotrexate. This led eventually to FDA approval of the drug for the treatment of RA [4,5].
IL-17A is the signature cytokine of Th17 cells and has pleiotropic effects on many cell types, inducing the upregulation of NF-κB, HLA class I, and several proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and GM-CSF. Of relevance to the pathogenesis of RA are the effects of IL-17 in driving osteoclastogenesis, leading to bone resorption [6]. Neutralization of IL-17A in mice decreased the severity of antigen-induced arthritis [7]. In addition, the severity of CIA is reduced in IL-17-deficient mice and mice administered IL-17-neutralizing antibodies [8].
Interleukin-2 plays a pro-inflammatory role in rheumatoid arthritis. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis had raised levels of sIL-2R both in their sera and in their synovial fluid compared to patients with osteoarthritis and age-matched healthy controls. Mononuclear cells from the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients were found to produce spontaneously high levels of sIL-2R which eluted at approximately m.w. 40,000 on gel filtration. In contrast, autologous peripheral blood cells only produced comparable levels upon stimulation with mitogenic lectin. Sequential studies indicated that serum sIL-2R levels were highly correlated with disease activity [9].
The Arthrinox/BIM-A capsule is composed of black sesame, guava fruit, mangosteen aril, pennywort leaves and soy protein; each of these components has the ability to increase collagen synthesis [10-13]. Interestingly, in the present study, we demonstrated that Arthrinox/BIM-A can modulate the immune cell functions by reducing the production of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-2, IL-17 and TNF-α. Arthrinox/BIM-A is therefore suggested as the food supplement for balancing immunity in the management of RA patients.
References
- David Fox A. Cytokine Blockade as a New Strategy to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis Inhibition of Tumor Necrosis Factor. Arch Intern Med. 2000; 160: 437-444.
- Matsuno H, Yudoh K, Katayama R, et al. The role of TNF-α in the pathogenesis of inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): a study using a human RA/SCID mouse chimera. Rheumatology. 2002; 41: 329-337.
- Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1993; 36: 1681-1690.
- Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Kalden JR, et al. Randomised double- blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994; 344: 1105-1110.
- Maini RN, Breedveld FC, Smolen JS, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of multiple intravenous infusions of anti-TNFα monoclonal antibody with or without weekly methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 41: 1552-1563.
- Kolls JK, Linden A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity. 2004; 21: 467-476.
- Koenders MI, Lubberts E, Oppers Walgreen B, et al. Blocking of interleukin-17 during reactivation of experimental arthritis prevents joint inflammation and bone erosion by decreasing RANKL and interleukin-1. Am J Pathol. 2005; 167: 141-149.
- Lubberts E, Koenders MI, van den Berg WB. The role of T-cell interleukin-17 in conducting destructive arthritis: lessons from animal models. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005; 7: 29-37.
- Nathan Wei. IL-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Immunology. 141: 2612-2618.
- Jirat Nganlasom, Tunda Suttitum, Dusit Jirakulsom hok, et al. Effect of Centella asiatica Linn. Leaves and Garcinia mangostana Linn. Hull on the healing of dermal wounds in diabetic rats. Srinagarind Med J. 2008; 23: 402-407.
- Tokudome Y, Nakamura K, Kage M, et al. Effects of soybean peptide and collagen peptide on collagen synthesis in normal human dermal fibroblasts. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2012; 63: 689- 95.
- Kishimoto Y, Saito N, Kurita K, et al. Ascorbic acid enhances the expression of type 1 and type 4 collagen and SVCT2 in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 430: 579-584.
- 13. Phitak T, Pothacharoen P, Settakorn J, et al. Chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of sesamin. Phytochemistry. 2012; 80: 77-88.